KKegiatan Knowing Sister 2021 dalam bentuk Study Club merupakan salah satu program kerja yang berbentuk Non Event dari Departemen Internal. Kegiatan ini wajib dihadiri oleh seluruh Mahasiswa Baru FKUB 2020. Knowing Sister dilaksanakan dalam dua rangkaian, dimana rangkaian pertama terdiri dari study club yang dilaksanakan sebelum UAB 1 dan UAB 2 untuk mempersiapkan mahasiswa kebidanan 2020 menghadapi ujian. Interaksi pertama dilaksanakan pada tanggal 14 dan 19 Maret 2021 dengan materi Ketrampilan Klinik Dasar dengan sub topik Sistem Kardiovaskular yang disampaikan dengan alat bantu power point. Sub topik sistem kardiovaskular yang menjadi topik bahasan yaitu mengenai pengertian, anatomi, fisiologi jantung, jumlah cairan yang terdapat di tubuh manusia, kandungan cairan, dan cara memperbaiki cairan yang hilang dalam tubuh. Meteri ini disampaikan oleh kakak- kakak tutor 2019, dimana mahasiswa kebidanan 2020 dibagi menjadi 10 kelompok dengan kakak tutor 1-3 orang. Di akhir sesi interaksi dilakukan sharing- sharing membahas materi dan topik yang ingin ditanyakan maba kepada kakak tutor.
Materi yang disampaikan :
Sistem kardiovaskular
- Sistem kardiovaskuler merupakan sistem tertutup artinya darah yang ditransportasikan akan berada di dalam jantung dan pembuluh darah, tidak dialirkan ke luar pembuluh darah.
- Sistem ini bertanggung jawab untuk mentransportasikan darah, yang mengandung nutrisi (Transport O2 dan nutrisi menuju sel dan Transport CO2 dari sel), bahan sisa metabolisme, hormone, zat kekebalan tubuh, dan zat lain ke seluruh tubuh. Sehingga, tiap bagian tubuh akan mendapatkan nutrisi dan dapat membuang sisa metabolismenya ke dalam darah
- Pergerakan komponen sistem imun (antibodi) : Menjamin pasokan zat kekebalan tubuh yang berlimpah pada bagian tubuh yang terluka, baik karena kecelakaan atau operasi, dengan bertujuan mencegah infeksi
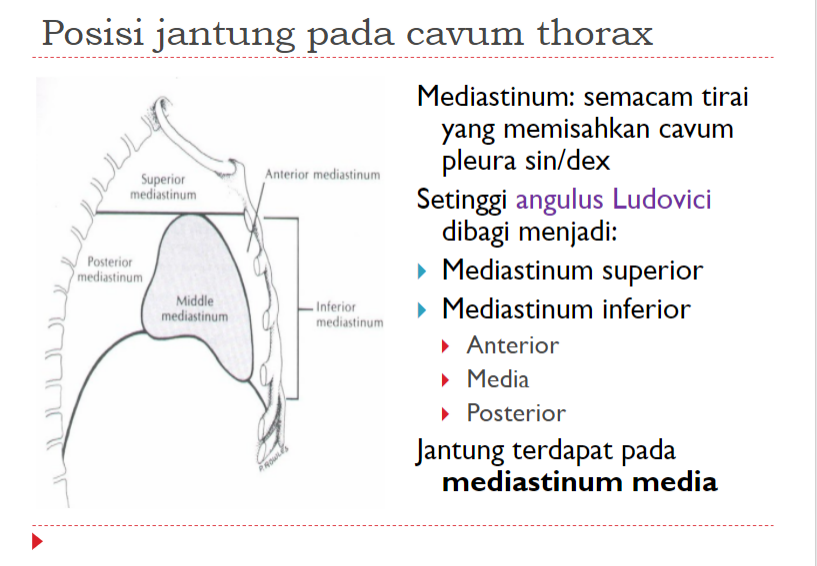
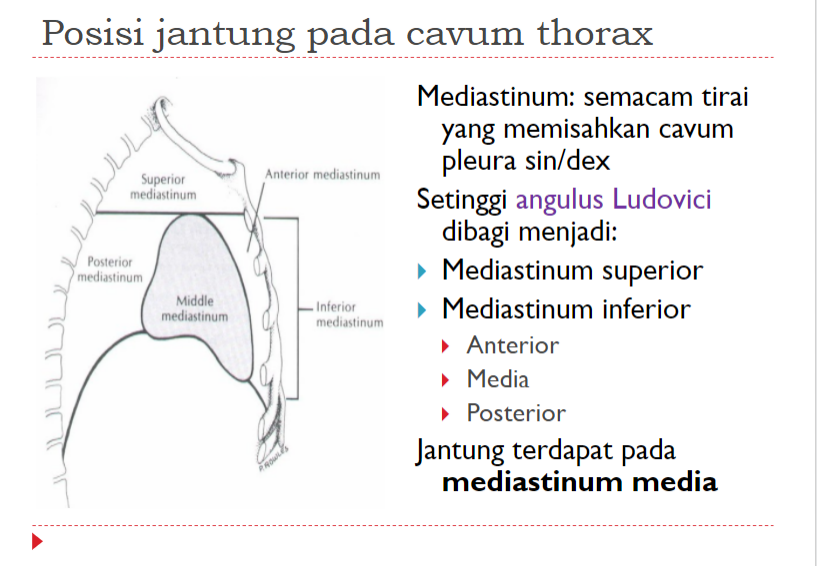
POSISI JANTUNG
Terletak di : mediastinum medial
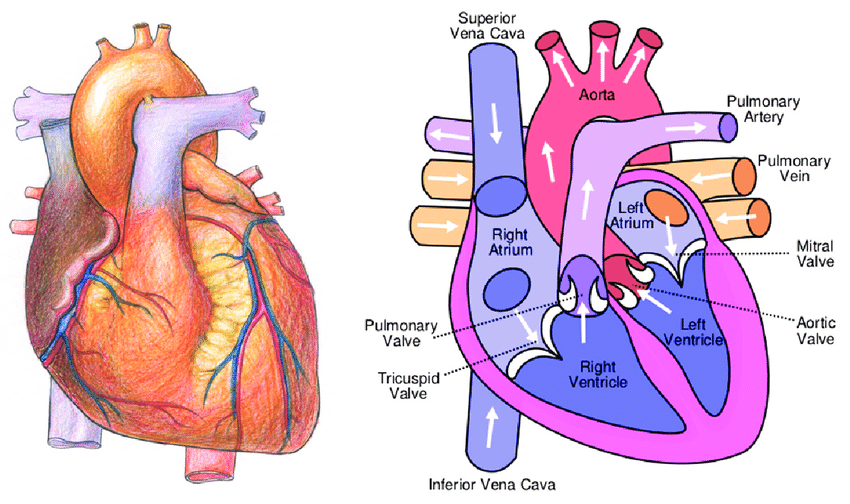
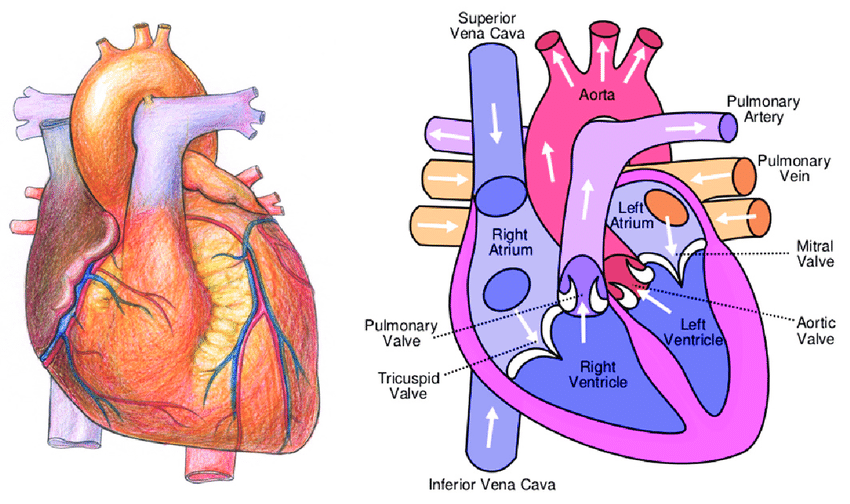
ANATOMI JANTUNG
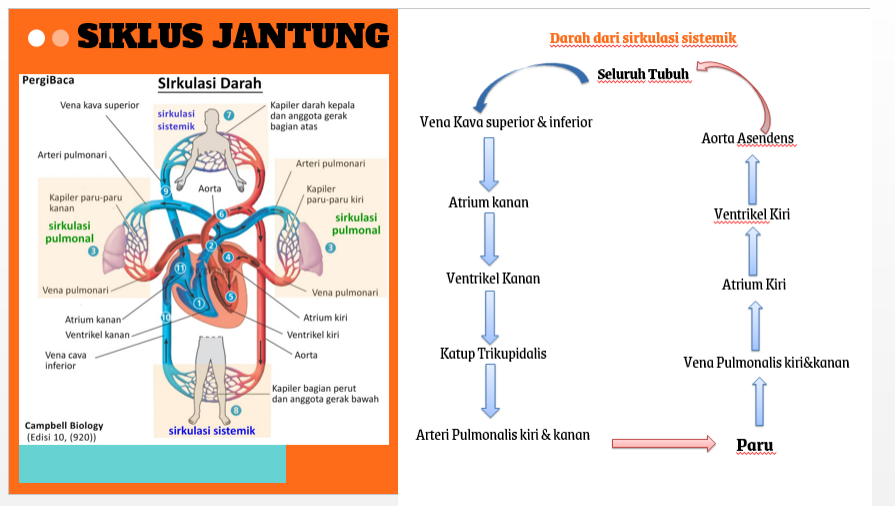
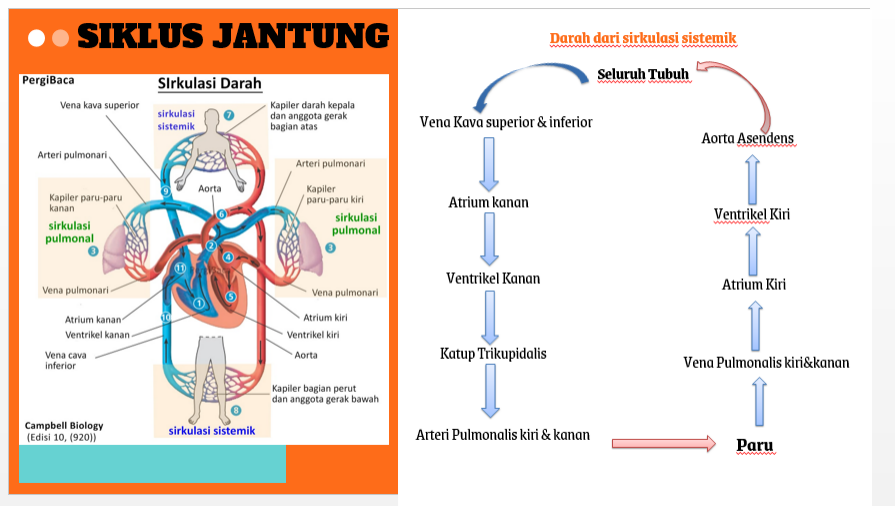
SIKLUS JANTUNG
Darah dari sirkulasi sistemik lewat vena cava superior dan inferior ⇒ atrium kanan ⇒ ventrikel kanan lewat katup trikuspidalis (katup AV kanan) ⇒ trunkus pulmonalis lewat katup semilunaris pulmonal ⇒ arteri pulmonalis kiri dan kanan ⇒ paru ⇒ vena pulmonalis kiri dan kanan ⇒ atrium kiri ⇒ katup mitral ⇒ ventrikel kiri ⇒ aorta asendens lewat katup semilunar aorta ⇒ seluruh tubuh ⇒ vena cava superior dan inferior
CONTOH KASUS 1
Tanggal Pengkajian: 26 Februari 2021
Seorang perempuan, umur 35 tahun, P2A0 datang ke PMB dengan keluhan nyeri perut Hasil pemeriksaan: KU lemah, TD 120/80 mmHg, N 90 x/menit, S 37,8 °C, P 18 x/menit. akral dingin.
Berapakah MAP pada perempuan tersebut ?
MAP = Diastolic pressure + 1/3 Sistole pressure
= 2/3 diastolic + 1/3 systolic
= 2/3 120 + 1/3 80
= 53,3 + 40
= 93,3
KASUS 2
Tanggal Pengkajian: 14 Maret 2021
Seorang perempuan, umur 25 tahun, P1A0 datang ke PMB dengan keluhan pusing kepala/ Hasil pemeriksaan: KU lemah, TD 110/70 mmHg, N 80 x/menit, S 37,8 °C, P 19 x/menit. akral dingin.
Berapakah MAP pada perempuan tersebut ?
MAP = Diastolic pressure + 1/3 Sistole pressure
= 2/3 diastolic + 1/3 systolic
= 2/3 110 + 1/3 70
= 83
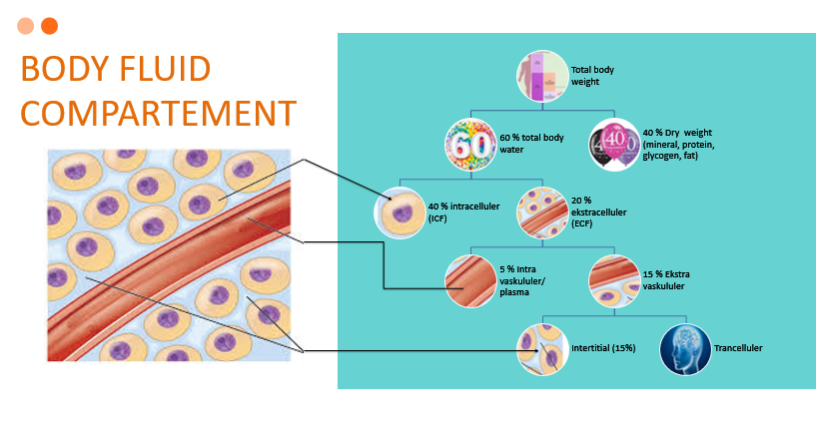
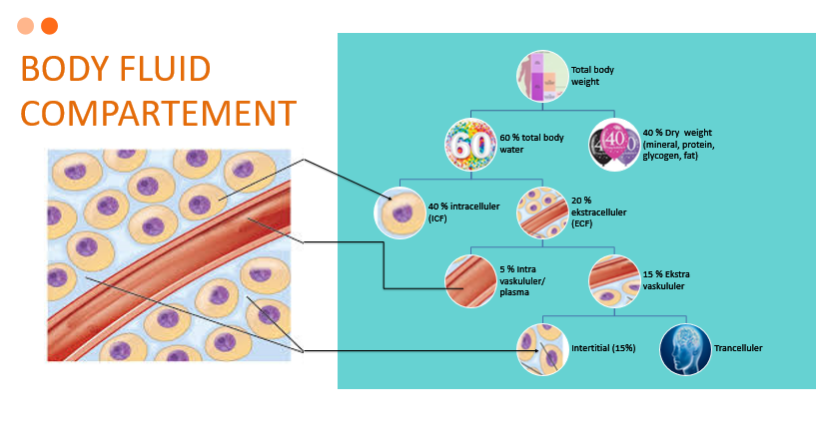
CAIRAN DALAM TUBUH
- Cairan intraseluler
Cairan mengandung sejumlah besar ion kalium dan fosfat ditambah ion magnesium dan sulfat dalam jumlah sedang, yang mana semua ion ini memiliki konsentrasi yang rendah di cairan ekstraseluler. Sel ini juga mengandung sejumlah besar protein, hampir empat kali jumlah protein dalam plasma.
- Cairan ekstraseluler
Komponen cairan ekstraseluler terdiri dari ion natrium, klorida dan bikarbonat yang jumlahnya banyak serta ditambah berbagai zat gizi untuk sel, seperti oksigen, glukosa, asam lemak, dan asam amino. Komponen penting dari cairan ekstraseluler adalah cairan interstisial, yang jumlahnya mencapai tiga perempat dari keseluruhan cairan ekstraselular, dan seperempat lainnya merupakan plasma
Tindakan Resusitasi
Diberikan segera untuk memulihkan sirkulasi ke organ vital setela kehilangan volume intravaskular karena perdarahan, kehilangan plasma, atau kehilangan cairan dan elektrolit eksternal yang berlebihan. Resusitasi cairan dapat dilakukan melalui oral, namun dengan kondisi pasien gawat darurat disarankan resusitasi cairan dilakukan secara intravena. Pemberian cairan secara intravena lebih efektif karena reaksi cepat langsung ke sistem sistemik, laju infus dapat dengan mudah diatur sesuai kebutuhan, mudah diberikan untuk pasien gawat darurat yang sulit atau tidak dapat menerima cairan secara peroral
Ex :
Sepsis, respon terhadap infeksi di dalam tubuh yang dapat berkembang menjadi sepsis berat dan syok septik ditandai rendahnya tekanan darah
KNOWING SISTER
The 2021 Knowing Sister activity in the form of a Study Club is one of the non-event work programs from the Internal Department. This activity must be attended by all new FKUB 2020 students. Knowing Sister is carried out in two series, where the first series consists of a study club which is held before UAB 1 and UAB 2 to prepare midwifery students 2020 for exams. The first interaction was held on March 14 and 19, 2021 with material on Basic Clinical Skills with the sub-topic of the Cardiovascular System which was delivered using power point tools. The sub-topics of the cardiovascular system which are the topics of discussion are the definition, anatomy, physiology of the heart, the amount of fluid present in the human body, fluid content, and how to repair lost fluids in the body. This metric was conveyed by the 2019 tutors, where the 2020 midwifery students were divided into 10 groups with 1-3 tutors. At the end of the interaction session, sharing was held to discuss the material and topic that the freshmen wanted to ask the tutor’s sister.
Material presented:
Cardiovascular system
- The cardiovascular system is a closed system meaning that the transported blood will be inside the heart and blood vessels, not flowed outside the blood vessels.
- This system is responsible for transporting blood, which contains it nutrition (Transport of O2 and nutrients to cells and Transport of CO2 from cells), metabolic waste materials, hormones, immune substances, and other substances throughout the body. So, every part of the body will get nutrients and can dispose of the rest of its metabolism into the blood
- Movement of immune system components (antibodies): Ensuring an abundant supply of immune substances to the injured part of the body, whether due to an accident or surgery, with the aim prevent infection
HEART POSITION
Located in: medial mediastinum
ANATOMY OF THE HEART
HEART CYCLE
Blood from the systemic circulation passes through the superior and inferior vena cavae ⇒ right atrium ⇒ right ventricle through the tricuspid valve (right AV valve) ⇒ pulmonary trunk through the pulmonary semilunar valve ⇒ left and right pulmonary arteries ⇒ lungs ⇒ left and right pulmonary veins ⇒ left atrium ⇒ mitral valve ⇒ left ventricle ⇒ ascending aorta through the semilunar valve of the aorta ⇒ whole body ⇒ superior and inferior vena cava
CASE EXAMPLE 1
Date of Assessment: 26 February 2021
A woman, age 35 years, P2A0 came to PMB with complaints of abdominal pain. Results of the examination: weak KU, BP 120/80 mmHg, N 90 x / minute, S 37.8 ° C, P 18 x / minute. cold akral.
What is the MAP of these women?
MAP = Diastolic pressure + 1/3 systole pressure
= 2/3 diastolic + 1/3 systolic
= 2/3 120 + 1/3 80
= 53.3 + 40
= 93.3
CASE 2
Date of Study: March 14, 2021
A woman, age 25 years, P1A0 came to PMB with complaints of headache / The results of the examination: weak KU, BP 110/70 mmHg, N 80 x / minute, S 37.8 ° C, P 19 x / minute. cold akral.
What is the MAP of these women?
MAP = Diastolic pressure + 1/3 systole pressure
= 2/3 diastolic + 1/3 systolic
= 2/3 110 + 1/3 70
= 83
LIQUID IN THE BODY
- Intracellular fluid
The liquid contains a large amount potassium and phosphate ions plus magnesium and sulfate ions in moderate amounts, which all these ions have a low concentration in the extracellular fluid. These cells also contain a large numberprotein, nearly four times the amount of protein in plasma.
- Extracellular fluid
The components of the extracellular fluid consist of sodium, chloride and bicarbonate ions which are large in number and plus various nutrients for cells, such as oxygen, glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids. An important component of extracellular fluid is interstitial fluid, which accounts for three-quarters of the total extracellular fluid, and the other quarter is plasma.
Resuscitation Measures
Administered immediately to restore circulation to vital organs after loss of intravascular volume due to bleeding, loss of plasma, or excessive loss of external fluid and electrolytes. Fluid resuscitation can be done orally, but in an emergency patient, it is recommended that intravenous fluid resuscitation be performed. Administration of fluids intravenously is more effective because of the rapid reaction directly to the systemic system, the infusion rate can be easily adjusted as needed, it is easy to administer to emergency patients who are difficult or unable to receive fluids orally
Ex:
Sepsis, a response to infection in the body that can develop into severe sepsis and septic shock characterized by low blood pressure
